Preparation of Alkanes:
1. Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation involves the addition of hydrogen to
unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes or alkynes) in the presence of a metal
catalyst such as Ni, Pd, or Pt, under elevated temperature (250°C).
2. Reduction of Alkyl Halides
Alkyl
halides can be reduced using zinc (Zn) in hydrochloric acid
(HCl) to form alkanes.
3. Hydrolysis of Grignard Reagents
Grignard
reagents (are highly reactive organometallic compounds that react with water to
produce alkanes. The reaction involves the cleavage of the carbon-metal bond,
and it must occur in the presence of dry ether as a solvent to
prevent premature hydrolysis of the Grignard reagent.
4. Corey-House
Synthesis
This is a coupling reaction of
alkyl halides with organo-metallic compounds, specifically lithium dialkyl
copper, to produce higher alkanes.
5. Reduction of
Carbonyl Compounds
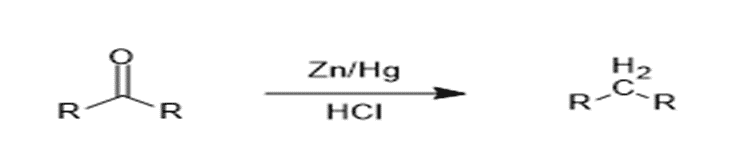
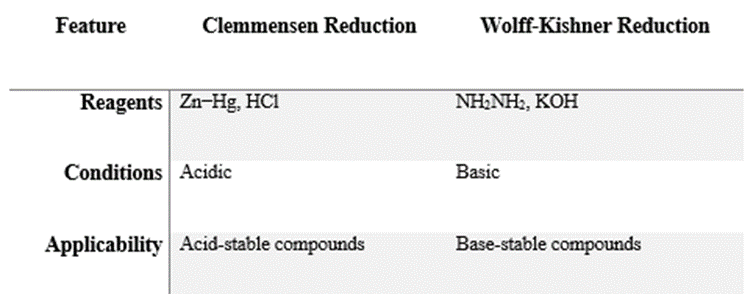
The reduction of carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) to alkanes can be achieved using two main methods: Clemmensen Reduction and Wolff-Kishner Reduction. These reactions differ in terms of the reagents, reaction conditions, and applicability.
1. Clemmensen Reduction
Clemmensen reduction involves
the reduction of aldehydes or ketones to alkanes using zinc amalgam
(Zn-Hg) in the presence of concentrated hydrochloric acid
(HCl). This method is suitable for compounds stable in acidic
conditions.
2.
Wolff-Kishner Reduction
Wolff-Kishner reduction converts aldehydes or ketones to alkanes by reacting them with hydrazine in the presence of a strong base (typically KOH/NaOH ) under high temperature.
Key
Differences:







No comments:
Post a Comment