Alkenes
Introduction
Alkenes
are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. They
follow the general formula CnH2n. A
double bond makes them unsaturated and more reactive than alkanes.
Olefins is another name for alkenes, derived from "olefiant gas" (oil-forming gas). This term historically referred to ethene () because it reacts with chlorine to form an oily liquid.
Properties of Alkenes
1.
Physical Properties:
o Insoluble
in water.
o Soluble
in organic solvents.
2.
Structure:
o Contains
a carbon-carbon double bond.
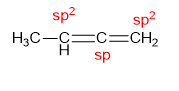
o Exhibits
sp² hybridization at the double-bonded carbons.
Like alkanes, alkenes are also subject to only
weak van der Waals attractive forces. The physical properties of alkenes are
therefore essentially similar to those of the corresponding alkanes. At room
temperature, the lower members of the family (alkenes containing upto 4 carbon
atoms) are gases, the members containing 5 to 17 carbon atoms are volatile
liquids and those containing 18 or more carbon atoms are solids.
The boiling points of alkenes are almost the same
as those of the corresponding alkanes, though slightly on the lower side.
Although alkenes are also less denser than water, their densities are always slightly
higher than those of the corresponding alkanes. The isomeric alkenes have very
close boiling points. It is difficult to separate them except with a very efficient
fractionating column, the straight chain 1-alkenes have boiling points a few
degrees lower than the straight chain alkenes with an internal double bond.
Classification of Alkenes
Alkenes
are classified based on the number of double bonds they contain:
- Monoenes:
- Alkenes with a
single double bond.
- Example: Ethene
(C2H4).
- Dienes:
- Alkenes with
two double bonds.
- Types of
dienes:
- Conjugated
Dienes: Double bonds
separated by a single bond (e.g., 1,3-butadiene).
- Cumulated
Dienes: Adjacent
double bonds (e.g., allene).
- Isolated
Dienes: Double bonds
separated by two or more single bonds.
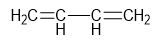


No comments:
Post a Comment