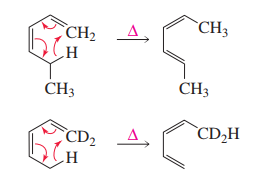
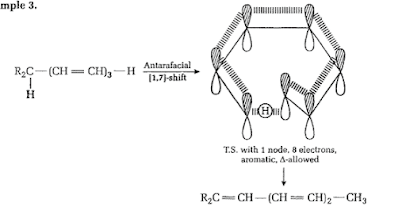
"From
Problem to Design: A Comprehensive Guide to Formulating and Designing Effective
Research Studies"
Research problem and research design are
crucial components of any research project. In this article, we will explore the key concepts of
research problem and research design, including how to formulate research
problem and objectives, types of research design, selection of appropriate
research design, and sampling techniques.
Formulating
Research Problem and Objectives:
Formulating a research problem involves
identifying a research question or issue that needs to be addressed. It is
important to clearly define the research problem and objectives to ensure that
the research is focused and targeted.
The research
objectives should be specific,
measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. This will help to
guide the research process and ensure that the research is conducted in a
systematic and objective manner.
Types
of Research Design:
There are several types of research
design that can be used, depending on the nature of the research problem and
objectives. These include:
Descriptive
research design: This type of research design is used to
describe and analyze the characteristics of a particular phenomenon or population.
Correlational
research design: This type of research design is used to
examine the relationship between two or more variables.
Experimental
research design: This type of research design is used to
test cause-and-effect relationships between variables,
through the use of controlled experiments.
Survey
research design: This type of research design is used to
gather data through the use of questionnaires or interviews.
Selection
of Appropriate Research Design:
The selection of an appropriate research
design is critical to the success of any research
project. The choice of research design should be based on the research problem and objectives, as well as the availability of resources and the feasibility of conducting
the research. Factors to consider when selecting a research design
include the nature of the research problem, the level of control required, the availability of participants, and the resources
available for data collection and analysis.
Sampling
Techniques:
Sampling techniques refer to the methods
used to select participants for a research study.
There are two main types of sampling techniques:
- Probability sampling
- Non-Probability sampling
Probability
sampling:
Probability sampling involves selecting participants randomly.
Non-Probability
sampling:
Non-probability sampling involves selecting participants based on certain criteria, such
as availability or willingness to participate.
The selection of a sampling technique
depends on the research problem and objectives,
as well as the availability of participants and
resources. Probability sampling is considered more
reliable and accurate, but may be more difficult
and costly to implement. Non-probability sampling may be more convenient and cost-effective,
but may be subject to bias and other limitations.
Conclusion:
Research problem and research design are
critical components of any research project. Formulating a clear research
problem and objectives is essential to guide the research process and ensure
that the research is focused and targeted. The selection of an appropriate
research design depends on the nature of the research problem and objectives,
as well as the availability of resources and the feasibility of conducting the
research. The choice of sampling technique is also important, as it can affect
the reliability and validity of the research findings. By understanding the key
concepts of research problem and research design, researchers can conduct their
studies in a systematic and objective manner, and generate meaningful insights
and contributions to their field of study.